

|
|
Clin. Cardiol. 23, 211–212 (2000)
This section edited by Edward A. Geiser, M.D.
Birke Schneider, M.D., and Karl-Heinz Kuck, M.D.
II. Medizinische Abteilung, Allgemeines Krankenhaus St. Georg, Hamburg, Germany
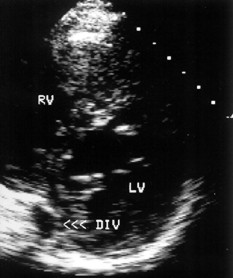
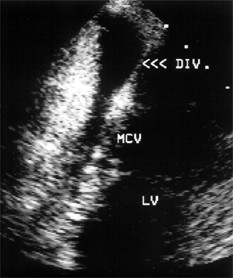
A 59-year-old man with a 20-year history of palpitations due to the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome was referred for radiofrequency catheter ablation. His 12-lead electrocardiogram showed a negative delta-wave polarity in leads III and aVF and a positive polarity in lead V1 consistent with a left posteroseptal accessory pathway (Fig.1). Transthoracic echocardiography demonstrated an echolucent area on the epicardial surface of the posteroseptal left ventricle in connection with the coronary sinus (Fig. 2A, arrows). Transesophageal echocardiography revealed a large middle cardiac vein entering a coronary sinus diverticulum 2.7 3 1.3 cm in size (Fig. 2B, arrows). Coronary sinus angiography confirmed the coronary sinus diverticulum and the presence of a large middle cardiac vein draining via the diverticulum into the coronary sinus, which was normal in size (Fig. 3). The accessory pathway was successfully ablated within the body of the coronary sinus diverticulum. Three years after the ablation the patient remains free of symptoms and his electrocardiogram shows normal conduction.
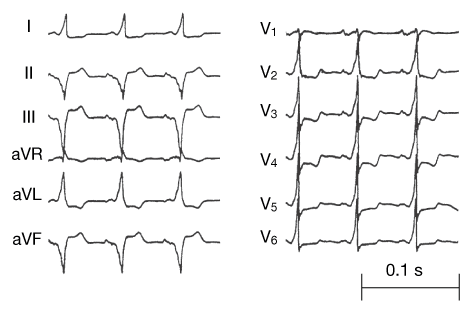 |
| Fig. 1 Twelve-lead electrocardiogram shows a preexcitation pattern consistent with a left posteroseptal accessory pathway. |
 |
 |
| A | B |
| Fig. 2 Transthoracic echocardiogram (A) from a parasternal short-axis view demonstrating the coronary sinus diverticulum (DIV, arrows) on the epicardial surface of the posteroseptal left ventricle (LV). Transesophageal image (B) from a transgastric long-axis view showing a large middle cardiac vein (MCV) draining into the coronary sinus diverticulum (DIV, arrows). RV = right ventricle. | |
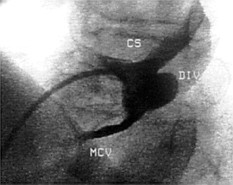 |
Fig. 3 Coronary sinus angiogram (left anterior oblique view) demonstrating the middle cardiac vein (MCV), which drains via the diverticulum (DIV) into the coronary sinus (CS). |
Reference
Address for reprints:
Birke Schneider, M.D.
II. Medizinische Abteilung
Allgemeines Krankenhaus St. Georg
Lohmühlenstrasse 5
20099 Hamburg, Germany
Received: March 9, 1999
Accepted with revision: May 3, 1999